DATA TYPES
Memory Locations for Data
• Identifier
– Name
– Rules for creating an identifier
• Combination of alphabetic characters (a-z and A-Z), numeric digits (0-9), and the underscore
• First character in the name may not be numeric
• No embedded spaces – concatenate (append) words together
• Keywords cannot be used
• Use the case of the character to your advantage
• Be descriptive with meaningful names
Reserved Words in C#
Naming Convention
• For Class, method, namespace, and property identifiers
– First letter of each word capitalized
• For Variables and Objects
– First letter of identifier lowercase; first letter of subsequent concatenated words capitalized
– First letter of variable name indicates its data type (I –int, f –float, d – double, b – boolean (not used in text)
– For Constant Literals
– All letters of identifier in upper case
– Underscore between words of identifier name
Variables
• Area in computer memory where a value of a particular data type can be stored
– Declare a variable
– Allocate memory
• Syntax – Simple Declaration
– type identifier; e.g.:
– double dTotSales;
• Syntax – Declaration &Compile-time initialization
– type identifier = expression; e.g.
– double dTaxRate = .125;
Types, Classes, and Objects
• Type
– C# has more than one type of number
– int type is a whole number
– floating-point types can have a fractional portion
• Types are actually implemented through classes
– One-to-one correspondence between a class and a type
– Simple data type such as int, implemented as a class
• Instance of a class → object
• A class includes more than just data
• Encapsulation → packaging of data and behaviors into a single or unit→class
Type, Class, and Object Examples
Predefined Data Types
• Common Type System (CTS)
• Divided into two major categories
Figure 3-1 .NET common types
Value and Reference Types
Figure 3-2 Memory representation for value and reference types
Value Types
• Fundamental or primitive data types
Figure 3-3 Value type hierarchy
Integral Data Types
• Primary difference
– How much storage is needed
– Whether a negative value can be stored
Floating-point Types
• May be in scientific notation with an exponent
• n.ne±P
– 3.2e+5 is equivalent to 320,000
– 1.76e-3 is equivalent to .00176
• OR in standard decimal notation
• Default type is double
Examples of Floating-point Declarations
double extraPerson = 3.50; // extraPerson originally set
// to 3.50
double averageScore = 70.0; // averageScore originally set
// to 70.0
double priceOfTicket; // cost of a movie ticket
double gradePointAverage; // grade point average
float totalAmount = 23.57f; // note the f must be placed after
// the value for float types
Decimal Types
• Monetary data items
• As with the float, must attach the suffix ‘m’ or ‘M’ onto the end of a number to indicate decimal
– Float attach ‘f’ or “F’
• Examples
decimal endowmentAmount = 33897698.26M;
decimal deficit;
Boolean Variables
• Based on true/false, on/off logic
• Boolean type in C# → bool
• Does not accept integer values such as 0, 1, or -1
bool undergraduateStudent;
bool moreData = true;













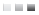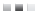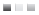

No comments:
Post a Comment